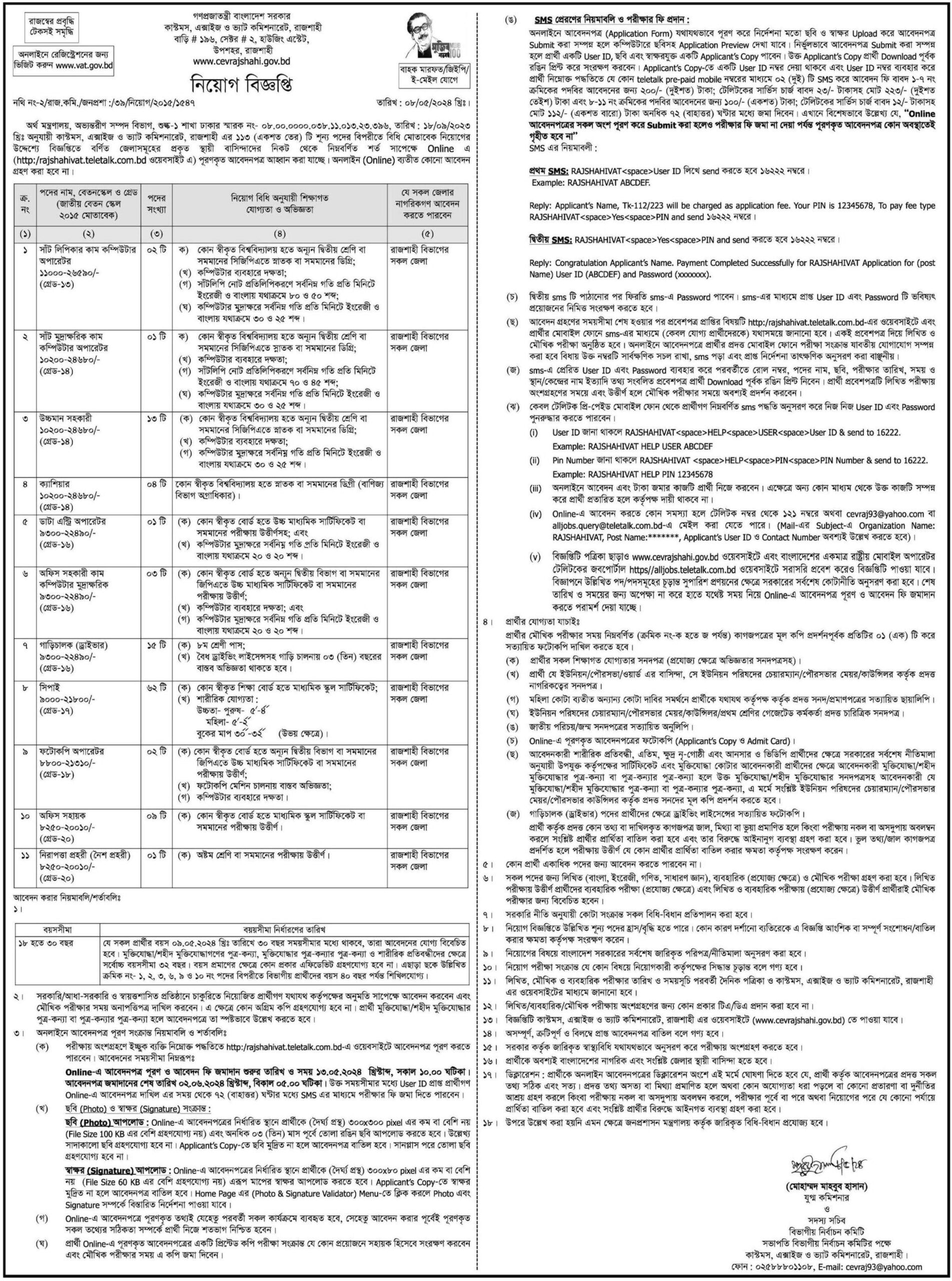
Customs Excise and VAT Commissionerate, Rajshahi
কাস্টমস, এক্সাইজ ও ভ্যাট কমিশনারেট, রাজশাহী
Job Category: Govt. Job
Job Source: দৈনিক প্রথম আলো
Posted On: 9 May 2024
Application Deadline:2 Jun 2024
Welcome to our website bangladeshtodays.org. This is the best website online. Here you will get daily updates on all types of job news such as: E.g Job Vacancies in Public Sector, Private Sector, Corporate, Banking, NGO Jobs etc. You can select any type of job from the category option in the top menu of the website. You can apply for jobs directly on our website.There is a search option at the top of this website where you can search for jobs according to your requirements. If you have benefited even in the slightest from our website, then you can tell your friends, family and everyone else about this website. I hope you also benefit from this website. You can share this website post on Facebook, Instagram, Twitter or any other online platform if you want. Many people can benefit from your sharing.And if there is anything you want to know or understand, you can contact us by email on the contact page of this website. We will try our best to help you, thank you very much.
### Customs, Excise, and VAT Commissionerate: Pillars of Revenue Administration
#### Introduction
The Customs Excise and VAT Commissionerate forms a crucial component of a nation’s revenue administration system. Tasked with the administration of customs duties, excise taxes, and value-added tax (VAT), these commissionerates play an essential role in economic regulation, revenue generation, and trade facilitation. Their functions encompass a broad spectrum of activities, from border control and anti-smuggling operations to tax compliance and policy enforcement. This comprehensive overview delves into the structure, functions, challenges, and future prospects of the Customs, Excise, and VAT Commissionerate.
#### Historical Background
The evolution of the Customs, Excise, and VAT Commissionerate is deeply intertwined with the history of trade and taxation. Historically, customs duties were among the earliest forms of taxation, imposed to regulate and protect domestic industries and generate revenue. Excise taxes, typically levied on the production and sale of specific goods like alcohol and tobacco, emerged later as a means to control consumption and raise funds. VAT, a more recent development, was introduced to streamline the taxation process on goods and services, ensuring a broad-based and efficient revenue collection mechanism.
#### Structure and Organization
The organizational structure of the Customs, Excise, and VAT Commissionerate is designed to ensure efficient administration and enforcement of tax laws. It typically includes several tiers of administration:
1. **Central Headquarters**: At the apex is the central headquarters, which formulates policies, oversees national operations, and coordinates with international bodies like the World Customs Organization (WCO) and the International Monetary Fund (IMF). This level is also responsible for major strategic decisions, international trade agreements, and compliance with global standards.
2. **Regional and Local Offices**: The central headquarters supervises regional and local offices that handle day-to-day operations. These offices are strategically located across the country, often at major ports, airports, and industrial hubs to facilitate trade and ensure compliance.
3. **Specialized Divisions**: Within the commissionerate, specialized divisions focus on distinct areas such as anti-smuggling, tax evasion investigations, audit and inspection, legal affairs, and taxpayer services. These divisions enable targeted and efficient handling of specific issues, enhancing the overall effectiveness of the organization.
#### Functions and Responsibilities
The Customs, Excise, and VAT Commissionerate performs a wide array of functions that are critical to the economic and fiscal health of a nation:
1. **Customs Administration**:
– **Border Control**: Ensuring the legal and efficient movement of goods across borders. This includes checking for compliance with import and export regulations, tariff classification, and collection of customs duties.
– **Trade Facilitation**: Simplifying and expediting the clearance of goods through initiatives like the Authorized Economic Operator (AEO) program and electronic customs clearance systems.
– **Anti-Smuggling Operations**: Preventing and investigating smuggling activities to protect national security, public health, and the economy.
2. **Excise Administration**:
– **Tax Collection**: Imposing and collecting excise taxes on specific goods such as alcohol, tobacco, and petroleum products. These taxes are typically levied at the production or import stage.
– **Regulatory Compliance**: Monitoring and ensuring compliance with excise laws, including licensing, production limits, and quality standards.
– **Control and Inspection**: Conducting regular inspections and audits to prevent tax evasion and ensure proper tax declarations by manufacturers and importers.
3. **VAT Administration**:
– **Registration and Compliance**: Ensuring that businesses required to register for VAT do so, and that they comply with the reporting and payment requirements.
– **Tax Collection**: Overseeing the collection of VAT at various stages of the supply chain, ensuring that taxes are accurately reported and remitted to the government.
– **Audit and Enforcement**: Conducting audits and investigations to detect and address VAT fraud, such as under-reporting of sales or fraudulent refund claims.
#### Challenges and Solutions
The Customs, Excise, and VAT Commissionerate faces numerous challenges in executing its mandate effectively:
1. **Complexity of Regulations**: The intricate nature of tax laws and regulations can create compliance challenges for businesses and enforcement difficulties for the commissionerate. Simplifying tax codes and providing clear, accessible guidance can help mitigate these issues.
2. **Technological Advancements**: Rapid technological changes, including e-commerce and digital transactions, pose new challenges for tax administration. Investing in modern IT infrastructure, data analytics, and digital tools can enhance the commissionerate’s ability to monitor and regulate these activities.
3. **International Trade Dynamics**: Global trade agreements, economic sanctions, and international cooperation efforts require constant adaptation and coordination. Engaging in international forums and bilateral cooperation agreements can help the commissionerate stay aligned with global standards and best practices.
4. **Resource Constraints**: Limited financial and human resources can impede the commissionerate’s operational efficiency. Securing adequate funding, investing in staff training.

