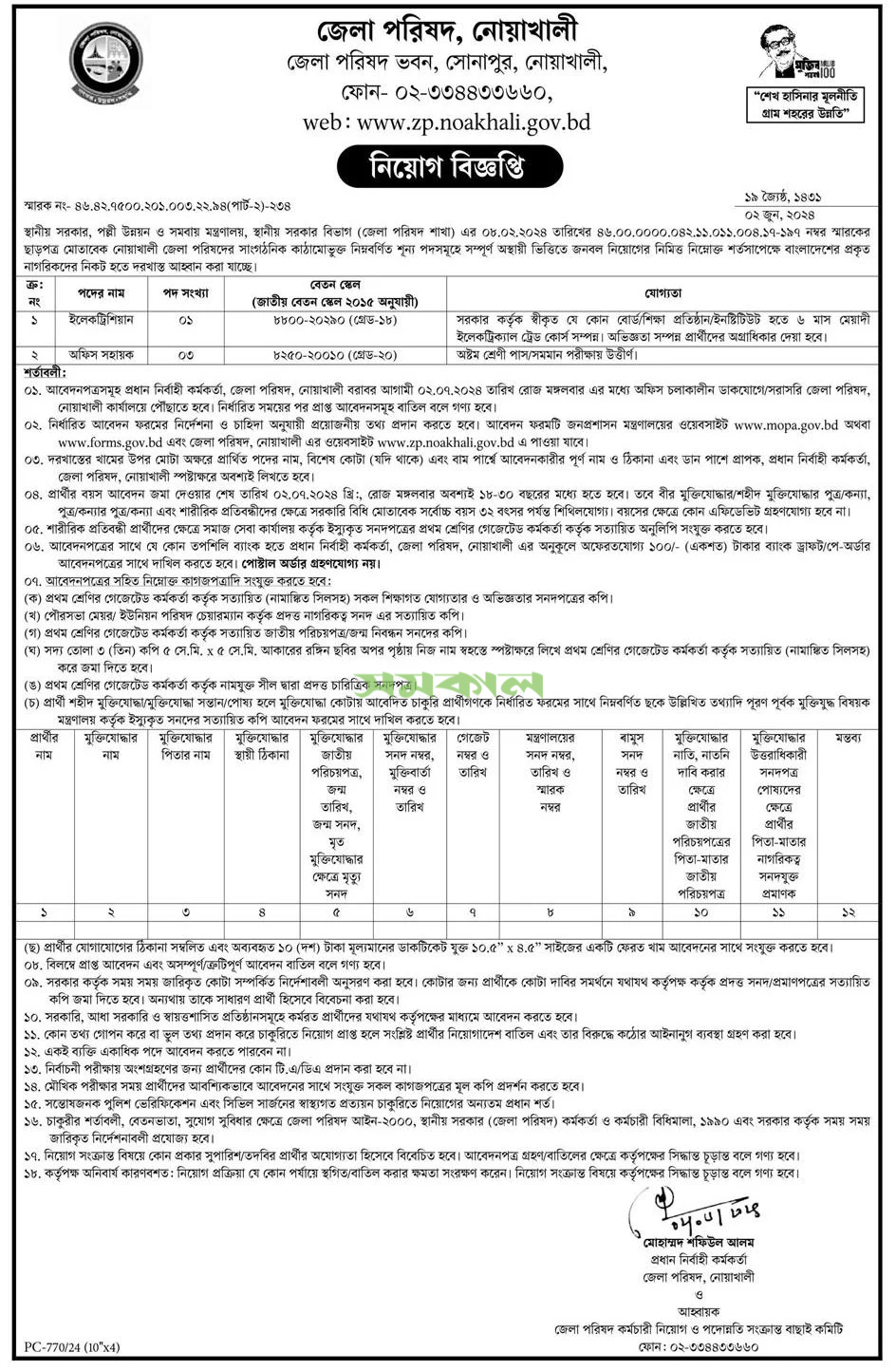
Zilla Parishad
জেলা পরিষদ
Job Category: Govt. Job
Job Source: দৈনিক সমকাল
Posted On: 3 Jun 2024
Application Deadline:2 Jul 2024
Welcome to our website bangladeshtodays.org. This is the best website online. Here you will get daily updates on all types of job news such as: E.g Job Vacancies in Public Sector, Private Sector, Corporate, Banking, NGO Jobs etc. You can select any type of job from the category option in the top menu of the website. You can apply for jobs directly on our website. There is a search option at the top of this website where you can search for jobs according to your requirements. If you have benefited even in the slightest from our website, then you can tell your friends, family and everyone else about this website. I hope you also benefit from this website. You can share this website post on Facebook, Instagram, Twitter or any other online platform if you want. Many people can benefit from your sharing. And if there is anything you want to know or understand, you can contact us by email on the contact page of this website. We will try our best to help you, thank you very much.
## District Councils: Pillars of Decentralized Governance
### Introduction
District Councils, known as Zilla Parishads in some countries, are vital institutions in the framework of decentralized governance. They serve as the intermediate tier of local government, positioned between the state or provincial governments and the grassroots village or municipal councils. District Councils play a crucial role in local administration, rural development, and community welfare. This essay explores the historical background, organizational structure, core functions, achievements, challenges, and future directions of District Councils, emphasizing their importance in governance and development.
### Historical Background
#### Origin and Evolution
The concept of local self-government has deep roots in many parts of the world, including the Indian subcontinent. The British colonial administration introduced local bodies such as district boards in the late 19th century to manage local affairs. These bodies were precursors to modern District Councils. Post-independence, many countries, including Bangladesh and India, formalized and expanded the role of these local institutions to strengthen democratic governance and promote grassroots development.
#### Post-Independence Reforms
Following independence, several countries restructured their local governance systems to enhance local autonomy and improve public service delivery. In Bangladesh, the Local Government (Union Parishad) Act of 1983 and subsequent reforms established a three-tier local government structure comprising Union Parishads (lowest tier), Upazila Parishads (intermediate tier), and Zilla Parishads (district level). Similar reforms occurred in India, with the 73rd and 74th Constitutional Amendments in 1992, which institutionalized Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRIs) and urban local bodies, respectively.
### Organizational Structure
District Councils operate under a structured framework designed to facilitate efficient administration and development at the district level. The organizational structure typically includes elected representatives, administrative officers, and various departments.
#### Elected Representatives
The governing body of a District Council comprises elected representatives from various administrative divisions within the district. Key positions include:
– **Chairperson**: The head of the District Council, elected by the council members, responsible for presiding over meetings and providing leadership.
– **Vice-Chairperson**: Assists the Chairperson and may act as the Chairperson in their absence.
– **Council Members**: Elected from different constituencies within the district, representing the interests of their constituents.
#### Administrative Officers
District Councils are supported by a team of administrative officers and staff who manage day-to-day operations. Key administrative positions include:
– **Chief Executive Officer (CEO)**: An appointed officer responsible for executing the council’s policies and decisions, overseeing administrative functions, and coordinating with various departments.
– **Finance Officer**: Manages the council’s finances, including budgeting, accounting, and financial reporting.
– **Development Officer**: Oversees development projects and programs, ensuring they align with the council’s objectives and priorities.
#### Departments and Committees
District Councils are organized into various departments and committees, each focusing on specific areas of administration and development. Common departments and committees include:
– **Education Department**: Manages primary and secondary education within the district, including the administration of schools and educational programs.
– **Health Department**: Oversees healthcare facilities and services, including hospitals, clinics, and public health initiatives.
– **Public Works Department**: Responsible for infrastructure development and maintenance, including roads, bridges, and public buildings.
– **Agriculture Department**: Supports agricultural development through extension services, training, and provision of resources to farmers.
– **Finance and Planning Committee**: Develops and monitors the council’s budget and financial plans.
– **Social Welfare Committee**: Implements programs and services for vulnerable and marginalized populations.
### Core Functions of District Councils
District Councils perform a wide range of functions aimed at promoting local development, improving public service delivery, and enhancing community welfare. These functions can be broadly categorized into administration, development planning, service delivery, and community engagement.
#### Administration
District Councils are responsible for the overall administration of the district, including:
– **Local Governance**: Enforcing local laws and regulations, maintaining law and order, and ensuring effective governance at the district level.
– **Resource Management**: Managing local resources, including land, water, and forests, in a sustainable manner.
– **Coordination**: Coordinating with state or provincial governments, other local bodies, and non-governmental organizations to implement policies and programs.
#### Development Planning
District Councils play a crucial role in planning and implementing development projects and programs. Key activities include:
– **Infrastructure Development**: Planning and executing projects to build and maintain infrastructure, such as roads, bridges, water supply systems, and sanitation facilities.
– **Economic Development**: Promoting economic activities, supporting small and medium enterprises (SMEs), and facilitating market access for local products.
– **Social Development**: Implementing programs to improve education, healthcare, and social welfare services, addressing the needs of vulnerable and marginalized groups.
#### Service Delivery
District Councils are tasked with delivering essential public services to the residents of the district. Key services include:
– **Education**: Administering primary and secondary schools, providing teacher training, and implementing educational programs to improve literacy and learning outcomes.
– **Healthcare**: Operating healthcare facilities, conducting health camps, and implementing public health initiatives to improve health outcomes.
– **Public Utilities**: Managing water supply, sanitation, and waste management services to ensure a clean and healthy environment.
#### Community Engagement
District Councils engage with the community to ensure that development initiatives align with local needs and priorities. Key activities include:
– **Public Consultations**: Organizing meetings and forums to gather input from residents on development plans and policies.
– **Awareness Campaigns**: Conducting campaigns to raise awareness about important issues, such as health, education, and environmental conservation.
– **Capacity Building**: Providing training and support to local leaders and community groups to enhance their capacity to participate in governance and development processes.
### Achievements of District Councils
Over the years, District Councils have made significant contributions to local development and governance. Some of the key achievements include:
#### Improved Infrastructure
District Councils have played a vital role in improving infrastructure within their jurisdictions. Key achievements include:
– **Road Construction**: Building and maintaining rural roads, bridges, and transportation networks, enhancing connectivity and accessibility.
– **Water Supply Systems**: Implementing projects to provide clean drinking water to rural and urban communities, reducing waterborne diseases and improving public health.
– **Sanitation Facilities**: Constructing public toilets, sewage systems, and waste management facilities to promote hygiene and environmental sustainability.
#### Enhanced Public Services
District Councils have made significant strides in enhancing public services, particularly in education and healthcare. Key achievements include:
– **School Infrastructure**: Building and upgrading schools, providing necessary facilities and resources to create a conducive learning environment.
– **Healthcare Services**: Establishing and managing healthcare facilities, conducting health camps, and implementing vaccination and disease prevention programs.
– **Social Welfare Programs**: Implementing programs to support vulnerable populations, including women, children, the elderly, and people with disabilities.
#### Economic Development
District Councils have contributed to economic development by promoting local industries and supporting small and medium enterprises. Key achievements include:
– **Agricultural Support**: Providing training, resources, and support to farmers to improve agricultural productivity and income.
– **Skill Development**: Implementing vocational training programs to equip residents with skills needed for employment and entrepreneurship.
– **Market Access**: Facilitating market access for local products through fairs, exhibitions, and trade initiatives, boosting local economies.
#### Community Empowerment
District Councils have empowered communities by involving them in governance and development processes. Key achievements include:
– **Participatory Planning**: Engaging residents in the planning and decision-making process, ensuring that development initiatives reflect local needs and priorities.
– **Capacity Building**: Providing training and support to local leaders, community groups, and civil society organizations to enhance their capacity to participate in governance and development.
– **Awareness Campaigns**: Conducting campaigns to raise awareness about critical issues, such as health, education, and environmental conservation, fostering informed and active citizenship.
### Challenges Faced by District Councils
Despite their achievements, District Councils face several challenges in fulfilling their mandate. These challenges include:
#### Financial Constraints
Limited financial resources can hinder the ability of District Councils to effectively carry out their functions. Key financial challenges include:
– **Inadequate Funding**: Insufficient budget allocations from higher levels of government can limit the scope and scale of development projects and services.
– **Revenue Collection**: Challenges in revenue collection, including low tax compliance and limited local revenue generation capacity, can constrain financial resources.
– **Expenditure Management**: Ensuring efficient and transparent management of financial resources to prevent misuse and corruption is a critical challenge.
#### Capacity Constraints
Capacity constraints, including limited human resources and technical expertise, can affect the performance of District Councils. Key capacity challenges include:
– **Staffing Issues**: Shortages of skilled and experienced staff can impact the efficiency and effectiveness of service delivery and project implementation.
– **Training and Development**: Limited opportunities for training and professional development can affect the capacity of council members and staff to perform their roles effectively.
– **Technical Expertise**: Lack of technical expertise in areas such as planning, engineering, and financial management can hinder the ability of District Councils to implement complex projects and programs.
#### Political Interference
Political interference and lack of autonomy can undermine the effectiveness of District Councils. Key political challenges include:
– **Centralization of Power**: Excessive centralization of power and decision-making authority at higher levels of government can limit the autonomy and effectiveness of District Councils.
– **Political Patronage**: Political patronage and interference in the appointment of council members and staff can affect the impartiality and performance of District Councils.
– **Conflict of Interest**: Conflicts of interest and political rivalries among council members can impact the decision-making process and hinder the implementation.

